Skin cancer remains a significant health concern in Australia, with the country holding one of the highest rates globally. Melanoma, a particularly aggressive form of skin cancer, is notably prevalent.
Why Early Detection Matters
The emphasis on early detection is driven by its potential to drastically improve treatment success rates and survival chances.Current Approaches to Early Detection
- Opportunistic screening
- Regular skin checks by healthcare professionals
Emerging Opportunities for Improvement
- Advancements in diagnostic technologies
- Leveraging artificial intelligence (AI)
Understanding Skin Cancer in Australia
Current Statistics on Skin Cancer Rates in Australia
Australia has one of the highest rates of skin cancer globally. The prevalence of melanoma in Australia is particularly alarming, with over 16,000 new cases diagnosed annually. Melanoma, often referred to as Australia’s national cancer, accounts for the majority of skin cancer-related deaths despite representing a smaller percentage of total skin cancer cases.Comparison Between Melanoma and Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers
Melanoma is not the only threat. Non-melanoma skin cancers (NMSC), including basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), are significantly more common. While less likely to be fatal, NMSCs contribute to a substantial healthcare burden due to their high treatment costs and frequent recurrences.Impact of Geographical and Demographic Factors on Skin Cancer Prevalence
Geographical and demographic factors play crucial roles in skin cancer prevalence. Regions like Canberra and Horsham see varying rates influenced by sun exposure levels, lifestyle choices, and access to healthcare facilities such as local clinics offering regular skin surveillance. For instance, our skin clinic in Broadbeach provides thorough skin checks to ensure early detection and treatment of any potential issues. Age also affects risk; older adults are more likely to develop both melanoma and NMSC due to cumulative UV exposure over time. Efforts such as promoting skin checks through platforms like the skin cancer check app aim to mitigate these risks by encouraging early detection across diverse Australian populations. Additionally, understanding individual allergies through methods like allergy skin prick testing can also play a role in tailoring skincare and prevention strategies.Current Approaches to Early Detection of Skin Cancer in Australia
Opportunistic Screening Methods
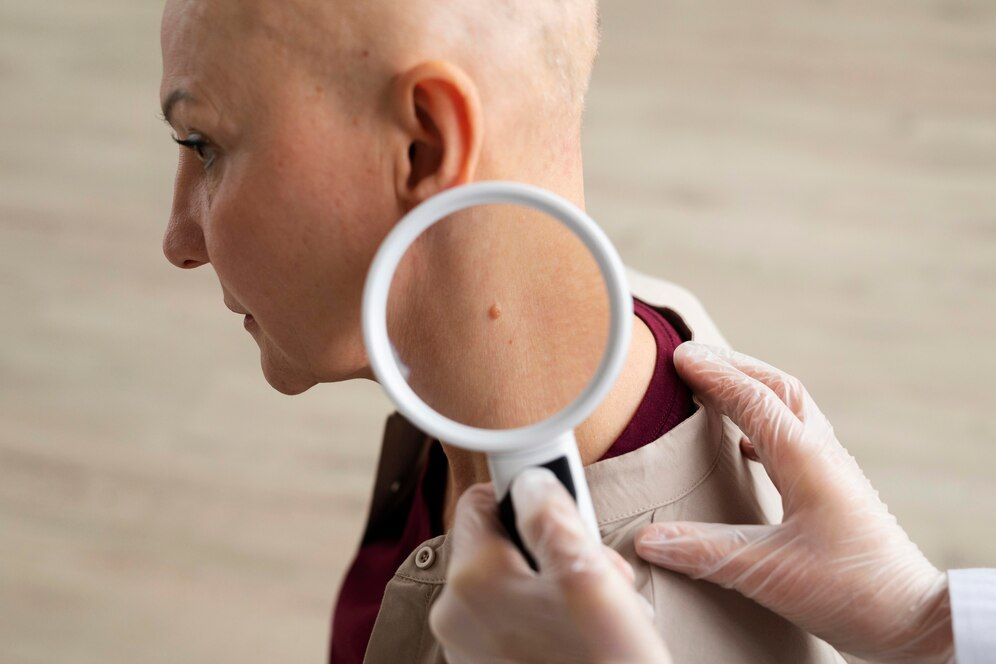
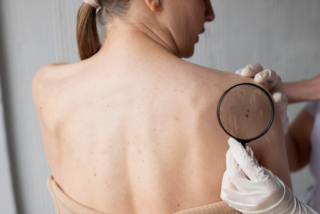
In Australia, opportunistic screening is a common approach for early detection of skin cancer. This method relies on individuals seeking skin checks based on personal or familial risk factors rather than through a systematic population-based screening program. Regular skin checks by healthcare professionals play a crucial role in identifying potential skin cancers at an early stage. These checks often involve:- Visual examination of the skin by dermatologists or trained general practitioners.
- Dermoscopic evaluation to identify suspicious lesions more accurately.
- Patient education on self-examination techniques to monitor changes in their skin.
Challenges in Early Detection
Despite the benefits, opportunistic screening faces several challenges:- Variable Care Quality: The quality of care can differ significantly depending on the healthcare provider’s experience and access to diagnostic tools. This variability may lead to inconsistent detection rates and potentially missed diagnoses.
- Sociodemographic Inequalities: Access to regular skin checks can be influenced by socioeconomic status, geographic location, and cultural factors. Individuals in rural and remote areas or from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may have limited access to dermatological services, which hinders early detection efforts.
- Health System Costs: The financial burden associated with frequent skin checks and follow-up procedures can strain both patients and the healthcare system. These costs include consultations, biopsies, and potential treatments for detected abnormalities.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Early Detection Capabilities
Diagnostic technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) are changing the game when it comes to detecting skin cancer early in Australia. AI algorithms are now being used to analyze dermoscopic images, making it much more accurate and efficient at spotting melanoma and other types of skin cancers. These technologies have the ability to see things that human eyes might overlook, acting as a crucial second opinion.Innovative Tools for Self-Examination
One of the exciting developments in this field is the rise of smartphone apps designed for self-examination. These apps are gaining popularity and allow individuals to keep track of any changes in their skin over time. Users can take high-resolution pictures of specific areas and compare them with a database containing known indicators of skin cancer. This approach puts power back into the hands of people, encouraging them to take proactive measures when it comes to monitoring their own health.Improving Access through Teledermatology
Another significant advancement is the introduction of teledermatology services, such as those offered by Broadbeach Family Practice. These services enable remote consultations with dermatologists, making it easier for individuals living in rural or underserved areas to receive expert care without having to travel long distances. Patients can simply upload images of their skin lesions, which are then reviewed by specialists who provide timely advice on whether further investigation or treatment is required.The Promise of Digital Technologies
The combination of these advancements in digital technologies and risk assessment tools has great potential for transforming how we detect skin cancer. By incorporating these innovations into regular healthcare practices, we can significantly increase the chances of diagnosing the disease earlier and achieving better outcomes for patients.Insights from the Melanoma Screening Summit: A Path Towards Improved Early Detection Strategies
The 2019 Melanoma Screening Summit underscored the necessity of a multifaceted approach to early detection, emphasizing both traditional methods and emerging technologies. Key findings pointed to:1. Genetic Risk Assessment
The summit highlighted the importance of incorporating genetic risk information into screening protocols. This involves identifying individuals with a higher predisposition to melanoma through genetic markers, allowing for more targeted and effective screening.2. Total Body Imaging and AI Algorithms
Discussions at the summit focused on integrating total body imaging with advanced AI algorithms. This combination aims to enhance early detection accuracy by providing comprehensive skin assessments that can identify suspicious lesions more reliably.3. Holistic Screening Methods
A call was made for holistic strategies that combine genetic data, clinical evaluations, and digital tools. This multifaceted approach is expected to improve overall outcomes by ensuring that high-risk individuals receive timely and accurate diagnoses. The insights from the Melanoma Screening Summit point towards an evolving landscape in skin cancer detection, driven by scientific advancements and a deeper understanding of genetic risk factors.Addressing Overdiagnosis Concerns: Striking a Balance Between Benefits and Harms in Opportunistic Screening Programs
Overdiagnosis of melanoma is a significant issue within opportunistic screening initiatives. This phenomenon occurs when screenings identify cancers that would not have caused harm during a patient’s lifetime, leading to unnecessary treatments and anxiety. Key points to consider:- Unnecessary Treatments: Overdiagnosis can result in patients undergoing surgical procedures, radiation, or chemotherapy that may not have been needed. These treatments carry risks and side effects.
- Psychological Impact: The emotional stress and anxiety associated with a cancer diagnosis can be profound, affecting the quality of life for individuals who might never have experienced symptoms.
- Resource Allocation: Healthcare systems may face strain due to increased biopsy rates and follow-up treatments for lesions that are ultimately benign or slow-growing.
Future Opportunities for Improvement in Early Detection Strategies for Skin Cancer Patients Across Diverse Australian Populations
There are several areas requiring further research to enhance early detection strategies for skin cancer in Australia. Identifying evidence gaps related to skin cancer risk prediction models is crucial. These models can guide targeted screening interventions, ensuring that high-risk individuals receive timely and appropriate care. Potential impacts of technological advancements on improving early detection strategies include:- AI-Powered Diagnostic Tools: AI algorithms can analyze skin images with high accuracy, potentially surpassing human diagnostic capabilities. These tools could be integrated into routine clinical practice to assist healthcare providers in identifying suspicious lesions more efficiently.
- Smartphone Applications: Consumer-driven digital technologies like smartphone apps facilitate skin self-examinations (SSE). These apps often provide reminders for regular checks and offer image analysis features that flag anomalies for further professional evaluation.
- Teledermatology Services: Remote consultations via teledermatology enable quicker access to specialists, particularly benefiting individuals in remote or underserved areas. This approach can bridge the gap caused by geographical and sociodemographic barriers, promoting equitable access to care.
Conclusion
Continued advancements in both scientific understanding and clinical practice are critical for achieving better outcomes for individuals at risk or diagnosed with skin cancer. The importance of early detection cannot be overstated. Leveraging cutting-edge technologies and integrating genetic risk assessments can significantly enhance early detection strategies. Collaborative efforts between researchers, clinicians, and community stakeholders are essential. By working together, we can ensure that innovations in diagnostic technologies are accessible to all Australians, regardless of geographical or socio-economic barriers. For instance, at Broadbeach Family Practice, we strive to provide comprehensive healthcare services including regular skin checks which play a vital role in early detection. Early detection of skin cancer in Australia – current approaches and new opportunities must remain a top priority. Embrace these advancements to reduce the impact of skin cancer and improve patient outcomes across diverse populations. Engage with your healthcare provider about regular skin checks at facilities like Broadbeach Medical Centre, stay informed about new technologies, and advocate for equitable access to these life-saving advancements. Moreover, it’s important to consider other health aspects such as allergies which may also affect overall well-being. The Allergy Clinic at Broadbeach Family Practice offers specialized services to address such concerns. Additionally, for those planning to travel, our Family Travel Clinic provides essential health services to ensure a safe journey.FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Why is early detection of skin cancer important in Australia?
Early detection of skin cancer is crucial as it significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and can reduce mortality rates. Given Australia’s high rates of skin cancer, prioritizing early identification can lead to better health outcomes.
What are the current approaches to early detection of skin cancer in Australia?
Current approaches include opportunistic screening, where healthcare professionals conduct regular skin checks. Additionally, advancements in diagnostic technologies and artificial intelligence are enhancing early detection capabilities.
What role do geographical and demographic factors play in skin cancer prevalence?
Geographical and demographic factors greatly influence the prevalence of skin cancer. Certain areas may have higher exposure to UV radiation, while demographic factors like age, ethnicity, and genetic predisposition also contribute to varying risk levels across populations.
What innovative tools are available for self-examination of skin cancer?
Innovative tools for self-examination include mobile applications that guide users through skin checks, as well as digital platforms that utilize AI to analyze images of moles or lesions for potential signs of skin cancer.
How does teledermatology improve access to skin cancer screening?
Teledermatology enhances access by allowing patients to consult dermatologists remotely. This approach is particularly beneficial for those in rural or underserved areas, facilitating timely evaluations and follow-ups without the need for extensive travel.
What are the future opportunities for improving early detection strategies in Australia?
Future opportunities include incorporating genetic risk assessments into screening programs, utilizing total body imaging with AI algorithms, and developing holistic strategies that combine various screening methods to cater to diverse Australian populations.